1.1 Elements of Programming instructs you on how to create, compile, and execute a Java program on your system.
1.2 Built-in Types of Data describes Java's built-in data types for manipulating strings, integers, real numbers, and booleans.
1.3 Conditionals and Loops introduces Java structures for control flow, including if-else statements, while loops, and for loops.
1.4 Arrays considers a data structure known as the array for organizing large quantities of data.
1.5 Input and Output extends the set of input and output abstractions (command-line arguments and standard output) to include standard input, standard drawing, and standard audio.
1.6 Random Web Surfer presents a case study that models the behavior of a web surfer using a Markov chain.
- Why Java?
The answer is that Java enables users to develop and deploy applications on the Internet for servers, desktop computers, and small hand-held devices. The future of computing is being profoundly influenced by the Internet, and Java promises to remain a big part of that future. Java is the Internet programming language.
- Java is a general purpose programming language
- Java is the Internet programming language
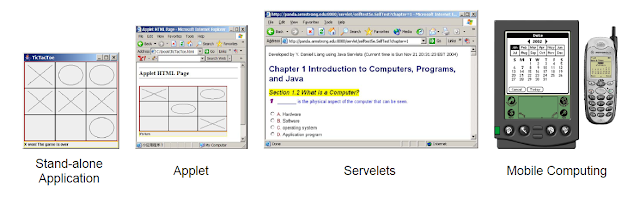
Java, Web, and Beyond
- Java can be used to develop Web applications
- Java Applets
- Java Servlets and Java Server Pages
- Java can also be used to develop applications for hand-held devices such as Palm cell phones
- James Gosling and Sun Microsystems
- Oak
- Java, May 20, 1995
- Hot Java : The first Java-enabled Web browser
Characteristics of Java
JAVA : A simple, object-oriented, distributed, interpreted, robust, secure, architecture neutral, potable, high-performance, multithreaded, dynamic language
- Java is simple
Java is partially modeled on C++, but greatly simplified and improved. Some
people refer to Java as "C++" because it is like C++ but with more functionality
and fewer negative aspects.
Java is inherently object-oriented. Although many object-oriented languages
began strictly as procedural languages, Java was designed from the start to be
object-oriented. Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a popular programming
approach that is replacing traditional procedural programming techniques.
One of the central issues in software development is how to reuse code. Object-oriented programming provides great flexibility, modularity, clarity, and reusability through encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
- Java is Object-oriented
Java is inherently object-oriented. Although many object-oriented languages
began strictly as procedural languages, Java was designed from the start to be
object-oriented. Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a popular programming
approach that is replacing traditional procedural programming techniques.One of the central issues in software development is how to reuse code. Object-oriented programming provides great flexibility, modularity, clarity, and reusability through encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
- Java is Distributed
Distributed computing involves several computers working together on a
network. Java is designed to make distributed computing easy. Since
networking capability is inherently integrated into Java, writing network
programs is like sending and receiving data to and from a file.
You need an interpreter to run Java programs. The programs are compiled
into the Java Virtual Machine code called bytecode. The bytecode is machineindependent
and can run on any machine that has a Java interpreter, which is
part of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Java compilers can detect many problems that would first show up at
execution time in other languages.
Java has eliminated certain types of error-prone programming constructs
found in other languages.
Java has a runtime exception-handling feature to provide programming
support for robustness.
Java implements several security mechanisms to protect your system
against harm caused by stray programs.
With a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), you can write one program that will run on any platform.
Because Java is architecture neutral, Java programs are portable. They can be run on any platform without being recompiled.
Java’s performance Because Java is architecture neutral, Java programs are portable. They can be run on any platform without being recompiled.
Multithread programming is smoothly integrated in Java, whereas in other languages you have to call procedures specific to the operating system to enable multithreading.
Java was designed to adapt to an evolving environment. New code can be loaded on the fly without recompilation. There is no need for developers to create, and for users to install, major new software versions. New features can be incorporated transparently as needed.






0 comments:
Post a Comment